XJTU and Xidian University researchers achieve breakthrough in 3D-printed high-performance piezoelectric materials devices
Piezoelectric devices are essential to modern medical diagnostics, industrial non-destructive testing, and smart sensing systems, while the high-performance optimization of key piezoelectric materials and their ability to form complex structures are both critical for practical applications.
Compared to traditional fabrication methods, such as mold forming and mechanical processing, 3D printing technology has demonstrated advantages in preparing complex and irregular piezoelectric ceramic components, including high-precision arrays and curved structures, due to its fast forming speed and high design flexibility.
However, the densification of 3D-printed piezoelectric ceramics remains a challenge, and their electrical performance still lags behind that of ceramics prepared using traditional methods, limiting the performance of 3D-printed piezoelectric devices and making it difficult for them to meet the demands of practical engineering applications.
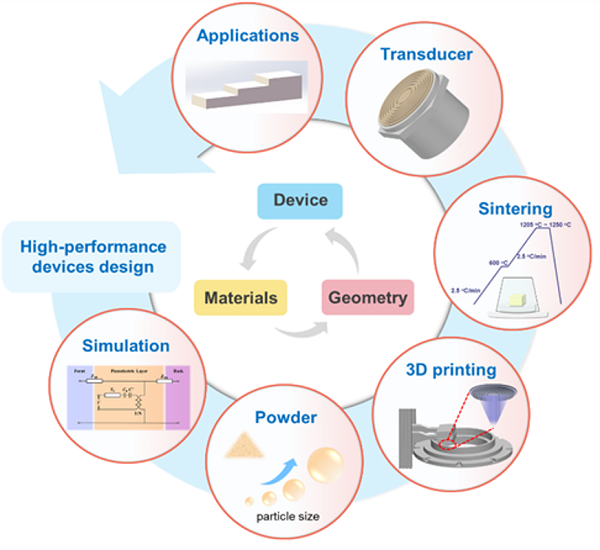
To address these issues, a team led by Academician Jiang Zhuangde from Xi'an Jiaotong University (XJTU) and Professor Yang Yintang from Xidian University has proposed a comprehensive design strategy for "piezoelectric material-complex structure-device application" based on 3D printing technology.
The team utilized digital light processing to manufacture high-performance Sm-doped PMN-PT piezoelectric ceramics, managing to form complex geometric structures and demonstrating advantages in ultrasonic transducer applications.
After optimizing the powder particle size, the curing performance was significantly improved, and the printed ceramic piezoelectric coefficient (d₃₃) reached as high as 1,285 pC/N. Furthermore, they designed and fabricated an eight-element ring array ultrasonic transducer that is difficult to achieve with traditional methods, showcasing a large bandwidth of 60 percent, a peak-peak voltage of 952 mV, and excellent imaging resolution.
This achievement is expected to provide new approaches for the customized design of piezoelectric devices for medical diagnostics and non-destructive testing.
The research findings were recently published in the internationally renowned journal Advanced Materials.
-
XJTU-USTC research team achieves breakthrough in pressure-sensitive phosphorescent polymers for smart materials
November 26,2025
-
XJTU and University of Cambridge achieve AI breakthrough in digital pathology
November 24,2025
-
XJTU researchers achieve advances in nonstationary time series analysis
November 19,2025

