Collaborative work by XJTU, UM and SCUT published in top math journal
Professor Chen Hongbin from the School of Mathematics and Statistics at Xi'an Jiaotong University (XJTU), in collaboration with Professor Gui Changfeng from the University of Macau and Associate Professor Yao Ruofei from South China University of Technology, had their paper Uniqueness of Critical Points of the Second Neumann Eigenfunctions on Triangles published online on Jan 13 in Inventiones Mathematicae, one of the world's top four mathematical journals.
This marks the second time since 2020 that a high-level achievement from XJTU's School of Mathematics and Statistics has been accepted by one of the top four mathematical journals in the world.
The paper focuses on the famous hot spots conjecture proposed by mathematician Jeffrey Rauch in 1974. This conjecture originates from the mathematical modeling of temperature diffusion in an insulated room. The temperature evolution satisfies the heat equation with Neumann boundary conditions, and over enough time, the temperature distribution is dominated by the second Neumann eigenfunction of the Laplace operator.
Thus, the hot spots conjecture can be equivalently stated as: In a simply connected planar region or a higher-dimensional convex region, the maximum and minimum values of the second Neumann eigenfunction can only be attained on the boundary of the region.
Although progress on this conjecture was slow for a long time, breakthrough results emerged by the end of the 1990s, including probabilistic methods based on reflected Brownian motion coupling, continuous methods combined with nodal line and harmonic analysis, probabilistic methods for Lipschitz domains, complex analysis methods for axisymmetric regions, and nonlinear equation analysis for perturbed disk regions.
Despite these advances, the conjecture for acute triangles remained unsolved in its entirety before this study. As the simplest planar region, triangles serve as a crucial testbed for research methods, making this problem a subject of intense focus and a long-standing, important conjecture recognized by the international mathematical community.
The conjecture involves multiple fields, including partial differential equations, spectral theory, mathematical physics, differential geometry, and Morse theory. Professor Chen and his collaborators' goal was not only to solve the conjecture, but also to establish a methodology applicable to studying the qualitative theory of related partial differential equations (such as the monotonicity and symmetry of mixed boundary value problems). After 13 years of hard work and persistence, with multiple stops and revisions along the way, they completed this work.
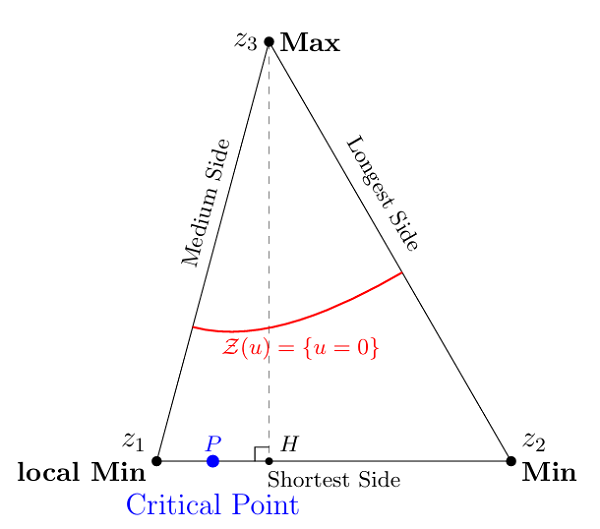
The study takes the second Neumann eigenfunction u of a planar triangle T as its object and proves that u has at most one non-vertex critical point and is monotonic along a certain direction within the triangle.
When T is non-equilateral, u takes the value zero at a vertex if and only if T is an "ultra-equilateral" triangle; while u has a non-vertex critical point if and only if T is acute and not ultra-equilateral.
These results verify the original theorem by Judge and Mondal, and solve the Polymath7 Project (Topic 1) goal concerning "extrema only at endpoints of the longest side", thus proving Siudeja's conjecture on the ordering of eigenvalues for the triangle's mixed Dirichlet-Neumann Laplacian. The entire proof employs various techniques, including the method of continuity, eigenvalue inequalities, the maximum principle, and the moving plane method.
-

XJTU holds 2026 New Year Concert
December 30, 2025
